
Are Sinus Infections Contagious?
Sinus infections, also known as sinusitis, are a common ailment affecting millions of people worldwide. Whether these infections are contagious is a frequent concern for those experiencing symptoms or in close contact with someone with sinusitis. This comprehensive guide will explore sinus infections’ nature, transmission, symptoms, and prevention strategies.
Understanding Sinus Infections
Sinus infections occur when the tissues lining the sinus cavities become inflamed or infected. The sinuses are hollow spaces in the skull and facial bones around the nose, producing mucus that helps moisturize nasal passages and trap foreign particles.
Types of Sinus Infections
- Acute sinusitis: Lasts up to 4 weeks
- Subacute sinusitis: Lasts 4-12 weeks
- Chronic sinusitis: Lasts more than 12 weeks or recurs frequently
Causes of Sinus Infections
- Viral infections (most common)
- Bacterial infections
- Fungal infections (rare)
- Allergies
- Structural issues in the nasal passages
Are Sinus Infections Contagious?
The answer to whether sinus infections are contagious is both yes and no, depending on the underlying cause.
Viral Sinus Infections
- Contagious: Yes
- Transmission: Through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks
- Spread: Can spread the virus causing the infection, but not the sinus infection itself
Bacterial Sinus Infections
- Contagious: Generally no
- Development: Often occurs as a secondary infection following a viral infection
- Transmission: Bacteria responsible for sinus infections can sometimes spread, but it’s less common
Non-Infectious Causes
- Contagious: No
- Examples: Allergies, environmental irritants, structural issues
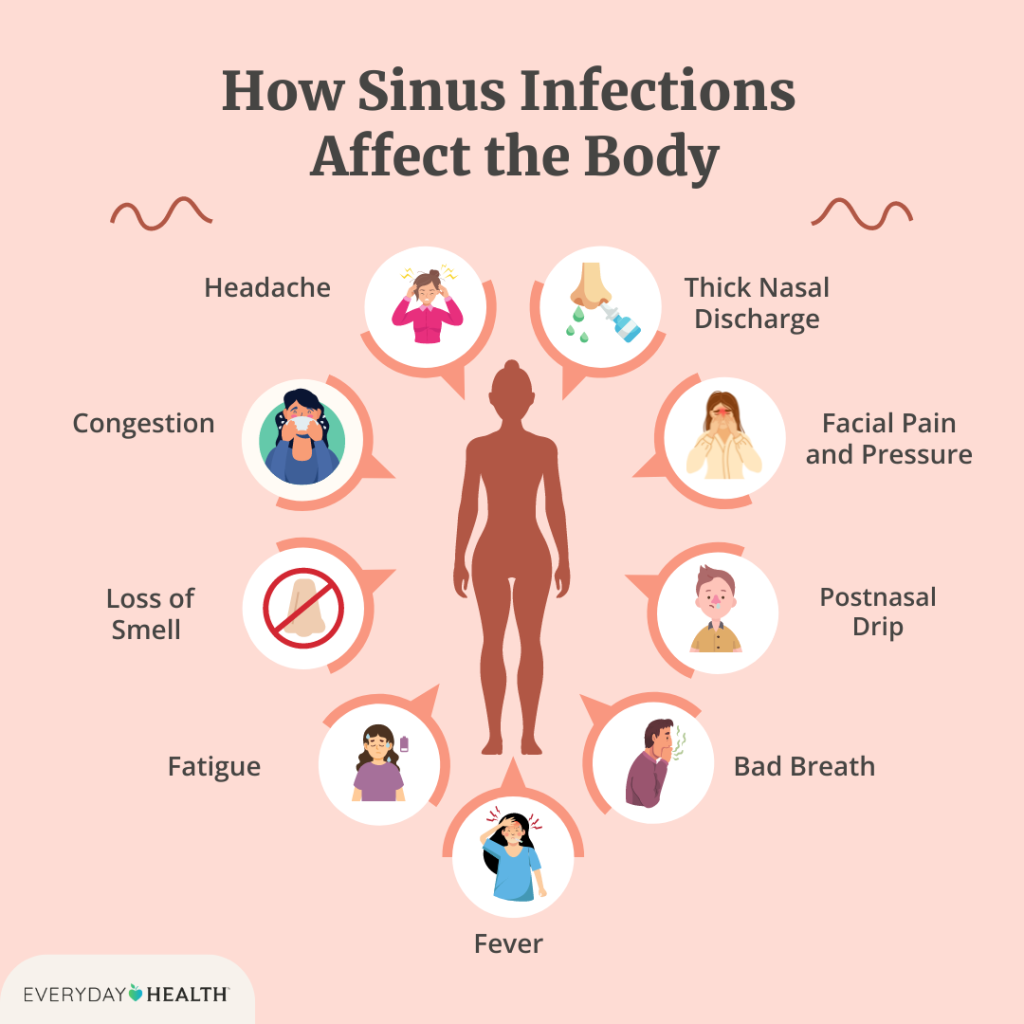
Symptoms of Sinus Infections
Common symptoms of sinus infections include:
- Facial pain or pressure
- Nasal congestion
- Thick, discoloured nasal discharge
- Reduced sense of smell
- Headache
- Fatigue
- Cough
- Sore throat
- Fever (in some cases)
Note: Symptoms can vary depending on the type and severity of the infection.
Transmission of Contagious Sinus Infections
When a sinus infection is caused by a contagious virus, it can spread through:
- Respiratory droplets: Released when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks
- Close contact: Touching or kissing an infected person
- Contaminated surfaces: Touching surfaces with the virus and then touching your face
Incubation and Contagious Period
- Incubation period: Varies depending on the virus, typically 1-4 days
- Contagious period: Usually begins before symptoms appear and lasts for 7-14 days
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis
Sinus infections are typically diagnosed based on symptoms and physical examination. In some cases, additional tests may be required:
- Nasal endoscopy
- Imaging studies (CT scan)
- Cultures of nasal discharge (in chronic cases)
Treatment
Treatment options depend on the cause and severity of the infection:
- Viral sinus infections:
- Rest and hydration
- Over-the-counter pain relievers
- Nasal decongestants
- Saline nasal irrigation
- Bacterial sinus infections:
- Antibiotics (if symptoms persist for more than 10 days or worsen after initial improvement)
- Supportive treatments, as mentioned, for viral infections
- Chronic sinusitis:
- Long-term antibiotics
- Nasal corticosteroids
- Allergy management
- In some cases, surgery may be necessary
Prevention Strategies
To reduce the risk of contracting or spreading sinus infections:
- Practice good hygiene:
- Wash hands frequently with soap and water
- Use hand sanitizer when soap is unavailable
- Avoid close contact with individuals who have respiratory infections.
- Cover your mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing.
- Stay home when you’re sick to prevent spreading the infection.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle:
- Get adequate sleep.
- Eat a balanced diet.
- Exercise regularly.
- Manage allergies effectively to reduce sinus inflammation.
- Stay hydrated to keep nasal passages moist.
- Use a humidifier to add moisture to the air, especially in dry environments.
- Avoid irritants like tobacco smoke and strong fragrances.
- Get vaccinated against influenza and other respiratory viruses.
When to See a Doctor
While many sinus infections resolve on their own, it’s important to seek medical attention if:
- Symptoms persist for more than 10 days
- Symptoms worsen after initial improvement
- You experience severe symptoms, such as high fever or severe facial pain
- You have recurrent sinus infections
Complications of Untreated Sinus Infections
Although rare, untreated sinus infections can lead to serious complications:
- Spread of infection to nearby structures (e.g., eyes, brain)
- Meningitis
- Brain abscess
- Osteomyelitis (bone infection)
Conclusion
Are Sinus Infections Contagious? While sinus infections themselves are not contagious, the viruses that often cause them can be. Understanding sinus infections’ nature, symptoms, and prevention strategies can help reduce the risk of contracting or spreading these infections.
You can effectively manage and prevent sinus infections by practising good hygiene, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and seeking appropriate medical care when needed.
Remember, if you experience persistent or severe symptoms, it’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.

